
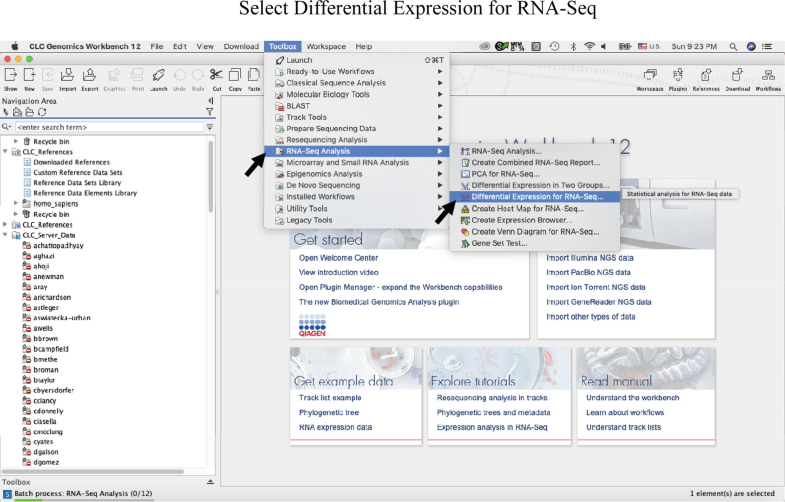
Sequence alignments can be stored in a wide variety of text-based file formats, many of which were originally developed in conjunction with a specific alignment program or implementation. For multiple sequences the last row in each column is often the consensus sequence determined by the alignment the consensus sequence is also often represented in graphical format with a sequence logo in which the size of each nucleotide or amino acid letter corresponds to its degree of conservation. In protein alignments, such as the one in the image above, color is often used to indicate amino acid properties to aid in judging the conservation of a given amino acid substitution. Many sequence visualization programs also use color to display information about the properties of the individual sequence elements in DNA and RNA sequences, this equates to assigning each nucleotide its own color. As in the image above, an asterisk or pipe symbol is used to show identity between two columns other less common symbols include a colon for conservative substitutions and a period for semiconservative substitutions. In text formats, aligned columns containing identical or similar characters are indicated with a system of conservation symbols. In almost all sequence alignment representations, sequences are written in rows arranged so that aligned residues appear in successive columns. These also include efficient, heuristic algorithms or probabilistic methods designed for large-scale database search, that do not guarantee to find best matches.Īlignments are commonly represented both graphically and in text format. These include slow but formally correct methods like dynamic programming. A variety of computational algorithms have been applied to the sequence alignment problem. Local alignments are often preferable, but can be more difficult to calculate because of the additional challenge of identifying the regions of similarity.
By contrast, local alignments identify regions of similarity within long sequences that are often widely divergent overall. Calculating a global alignment is a form of global optimization that "forces" the alignment to span the entire length of all query sequences. Computational approaches to sequence alignment generally fall into two categories: global alignments and local alignments. Instead, human knowledge is applied in constructing algorithms to produce high-quality sequence alignments, and occasionally in adjusting the final results to reflect patterns that are difficult to represent algorithmically (especially in the case of nucleotide sequences). However, most interesting problems require the alignment of lengthy, highly variable or extremely numerous sequences that cannot be aligned solely by human effort. Very short or very similar sequences can be aligned by hand. Although DNA and RNA nucleotide bases are more similar to each other than are amino acids, the conservation of base pairs can indicate a similar functional or structural role. The absence of substitutions, or the presence of only very conservative substitutions (that is, the substitution of amino acids whose side chains have similar biochemical properties) in a particular region of the sequence, suggest that this region has structural or functional importance.

In sequence alignments of proteins, the degree of similarity between amino acids occupying a particular position in the sequence can be interpreted as a rough measure of how conserved a particular region or sequence motif is among lineages.
If two sequences in an alignment share a common ancestor, mismatches can be interpreted as point mutations and gaps as indels (that is, insertion or deletion mutations) introduced in one or both lineages in the time since they diverged from one another. 6.5 Techniques inspired by computer science.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
